Featured Post
System interface questions for requirement elicitation - Business analyst/System analyst
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Generic overview of
questions to ask for the specification of an interface (between a system A and
a system B) – Business Analyst/System Analyst
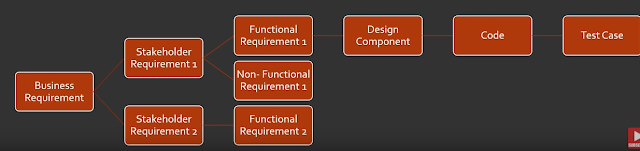
Ø Business Requirement Questions
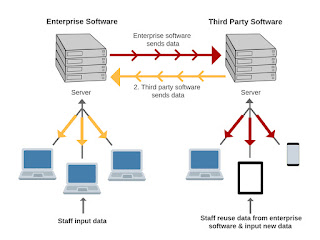
1. What kind of interface do you need unidirectional or bidirectional
- Unidirectional interface: The data will be sent in one direction by the sender to the receiver.
- Ex: System A sends data to System B and the receiver System B will read, process, write and store the data.
- In the case of bidirectional the systems are connected such that data can be sent and received by both.
- Ex: System A and System B can both read, process, write, and store the data within each other.
2.
What do you want to
achieve with this interface?
The business
needs this interface to help to fulfill and provide support.
3.
The Actions Needed by
you in the interface?
- The data is required to be
- Deleted (DELETE),
- Overridden and created (PUT),
- Overridden, created, appended (POST)
- Read the Data (GET)
4.
How will
authentication between two systems takes place?
In case of source the system wants to change something in the receiver, what will be the authentication
rights provided (Ex: Read-only Access, read and write access). To be deeply
thought in relation to the bidirectional interface.
 |
| Analyst Humor |
5.
Do you have any existing
interface design and standards in mind?
6.
Does the source system
have system logs, and will they be made accessible?
Ø Data Integration Questions
7.
What is the data that
the target system requires to complete the integration task?
- Identifying the target data is an important first step.
- It helps in defining the objects or tables that are needed to be
accessed, and the rules the data needs to comply with.
-
Typically, the target data model drives the design of a custom
integration point, should one be required.
8.
Where is the data
required by the target system located in the source system?
-
In Files, Objects, Database, Other third-party apps, etc.
9.
What are the probable data
transformations needed?
- Common examples of data types that need to be transformed are
numbers and dates.
- For example, date formats and time zones may be different between
the systems and needed to be converted.
10. What is the general quality of the data? Is it accurate? Complete?
Recent? Unique or redundant?
Ø Transaction Questions
11. What is considered a transaction within the integration task?
- A transaction is an atomic unit of work.
- It only changes the state of the target system if the data was successfully transferred and processed.
- If any failure occurs, whether it is during the transport or
processing (i.e. validation), it must be ensured that the target system remains
unchanged.
12. Are there any dependencies between transactions?
·
For example, if a transaction creates multiple records in the
target system (i.e. an account and a contact, and the account was successfully
created but the contact failed the validation), it must be ensured that the
account record is removed again.
·
This way the target system has the same state at the end of the
transaction as when it started.
13. Does the system facilitate recovery procedures in the event of
system failure? (For example, roll back
to the last completed transaction).
Ø Connectivity Questions
14. How will you connect to the target system (Connectivity
Constraint)?
· The Domain name, IP, etc.
15. What security constraints apply (certificates, credentials, etc.)?
·
It is better to identify and verify them during the project start. As
these can lead to various delays or blockers.
·
The reasons are manifold like missing firewall rules, required
certificates, setup of new security roles and credentials, protocol
incompatibilities between source and target system – just to name a few.
·
From a technical perspective, most of those issues can be
resolved. But it is often the processes or additional constraints that are only
identified during the validation, which add more risk and effort to the system
integration project.
Ø Architecture Questions
16. What interface options do you have available (REST, SOAP, RPC, Custom,
etc.)?
·
The interface options have an impact on the tools and
implementation design.
·
This is because they help determine whether the solution must be
entirely custom or whether productized solutions are an effective system
integration method.
·
Creating the right design may not always include the path of
the simplest or most straightforward solution.
17. Are there any obsolete technology being used in the Source
System?
·
In case of use of an obsolete the technology of data from the source system.

Comments
Post a Comment
Let's discuss and learn more